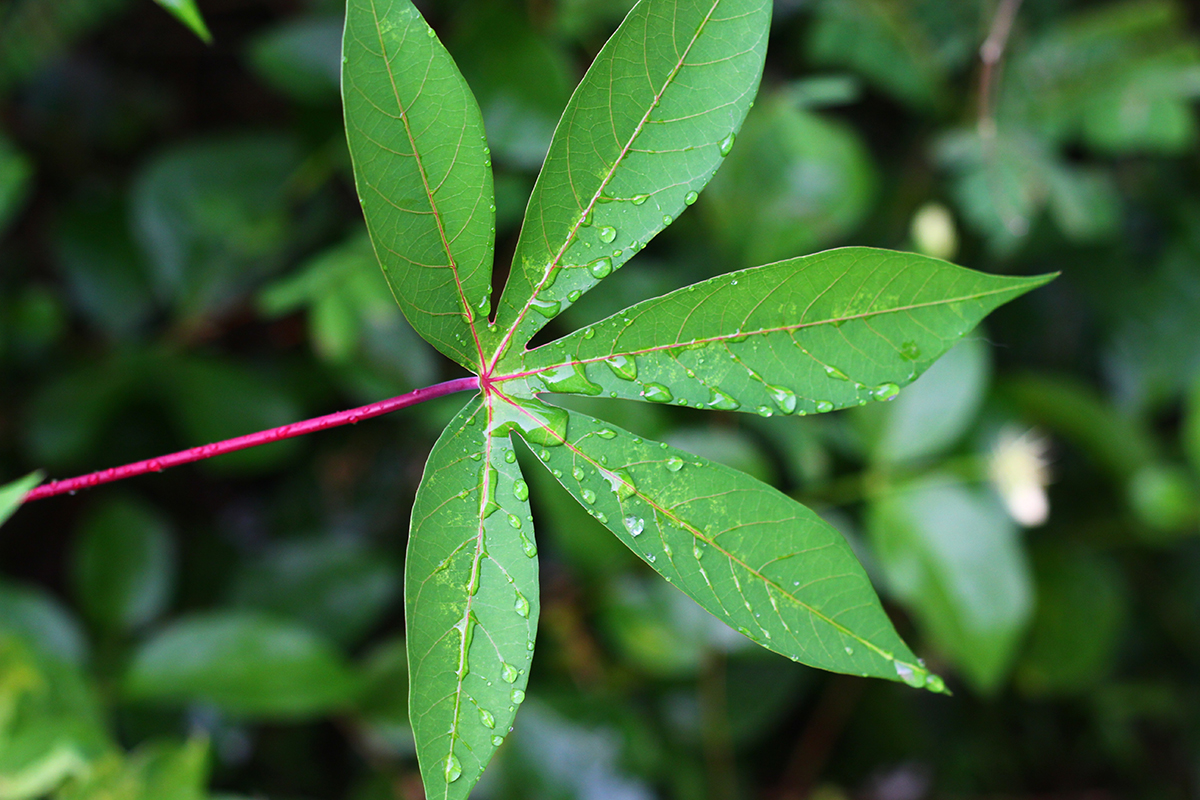
Cassava Leaf Magic: How to Incorporate This Nutritious Green into Your Garden and Meals – you might be familiar with the starchy cassava root, but have you discovered the magic of its leaves? Beyond their vibrant green hue, cassava leaves are a nutritional powerhouse packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, making them a delicious and healthy addition to your diet.
This versatile green can be enjoyed in a variety of ways, from traditional recipes passed down through generations to innovative culinary creations. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or a curious beginner, we’ll guide you through cultivating these leafy wonders in your own backyard and unlock the secrets of incorporating them into your meals.
From planting and caring for cassava plants to exploring different ways to prepare them, we’ll cover everything you need to know to unlock the magic of cassava leaves. Join us as we delve into the fascinating world of this nutritious green, where culinary adventures and health benefits intertwine.
Get ready to transform your garden and your plate with the power of cassava leaves.
Cassava Leaf: A Nutritional Powerhouse
Cassava leaves, also known as Manihot esculenta, are a leafy green vegetable that is a staple food in many parts of the world, particularly in Africa, Asia, and South America. While the starchy root of the cassava plant is commonly consumed, the leaves are often overlooked, despite their impressive nutritional value.
Nutritional Profile of Cassava Leaves
Cassava leaves are an excellent source of essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. They are particularly rich in:
- Vitamin A:Cassava leaves are an excellent source of vitamin A, which is crucial for maintaining healthy vision, skin, and immune function. A 100-gram serving of cassava leaves provides approximately 10,000 IU of vitamin A, which is more than the daily recommended intake for adults.
- Vitamin C:Cassava leaves are also a good source of vitamin C, a powerful antioxidant that helps protect cells from damage and boosts the immune system. A 100-gram serving of cassava leaves contains about 30 mg of vitamin C, which is about 33% of the daily recommended intake.
- Iron:Cassava leaves are rich in iron, an essential mineral for red blood cell production and oxygen transport. A 100-gram serving of cassava leaves provides about 2.5 mg of iron, which is about 14% of the daily recommended intake for men and 20% for women.
- Calcium:Cassava leaves are also a good source of calcium, a mineral that is essential for strong bones and teeth. A 100-gram serving of cassava leaves contains about 100 mg of calcium, which is about 10% of the daily recommended intake.
- Antioxidants:Cassava leaves are rich in antioxidants, which help protect the body from damage caused by free radicals. These antioxidants include flavonoids, carotenoids, and phenolic compounds.
Comparison with Other Leafy Greens, Cassava Leaf Magic: How to Incorporate This Nutritious Green into Your Garden and Meals
Cassava leaves compare favorably to other leafy greens in terms of their nutritional content. For example, a 100-gram serving of cassava leaves provides more vitamin A than spinach, kale, and collard greens. They also contain more iron than spinach and kale.
Versatility in Cuisines
Cassava leaves are a versatile ingredient that can be incorporated into various cuisines. They can be boiled, steamed, fried, or sautéed. Here are some meal ideas that showcase the versatility of cassava leaves:
- Cassava Leaf Soup:This hearty soup is a popular dish in many African countries. It is typically made with cassava leaves, tomatoes, onions, and spices.
- Cassava Leaf Stew:This flavorful stew is another popular dish in Africa. It is made with cassava leaves, meat, fish, or vegetables, and seasoned with spices.
- Cassava Leaf Salad:Cassava leaves can be added to salads for a boost of flavor and nutrients. They can be served raw or cooked.
- Cassava Leaf Pancakes:Cassava leaves can be used to make pancakes or fritters. They are typically mixed with flour, eggs, and spices.
Cultivating Cassava Leaves in Your Garden

Cassava leaves, a nutritious and versatile ingredient, can be easily grown in your own garden. Understanding the optimal growing conditions and following proper planting and care practices will ensure a bountiful harvest of these leafy greens.
Growing Conditions for Cassava Leaves
Cassava leaves thrive in warm climates with ample sunlight and well-drained soil. The ideal temperature range for optimal growth is between 25°C and 30°C (77°F and 86°F). Cassava plants are known for their adaptability and can tolerate a wide range of soil types, but they prefer sandy loam or clay loam soils with good drainage.
These soils allow for proper aeration and prevent root rot, which can occur in waterlogged conditions. Cassava plants require at least 6 hours of direct sunlight daily for healthy growth and leaf production. In areas with less sunlight, they may grow, but leaf production may be reduced.
Sunlight helps in photosynthesis, which is crucial for the plant’s energy production and overall growth.
Planting Cassava
- Choose a suitable location:Select a sunny spot in your garden with well-drained soil. Avoid planting cassava in areas prone to waterlogging or flooding.
- Prepare the soil:Dig a hole about 15-20 cm (6-8 inches) deep and wide. Loosen the soil and incorporate compost or manure to improve drainage and nutrient content.
- Plant the cassava cuttings:Cassava plants are propagated using cuttings. Select healthy cassava stems with at least 3-4 nodes. Cut the stem into pieces of about 15-20 cm (6-8 inches) long. Plant the cuttings vertically in the prepared holes, ensuring that at least two nodes are buried in the soil.
- Water thoroughly:After planting, water the cassava cuttings generously to help them establish roots.
Caring for Cassava Plants
- Watering:Water the cassava plants regularly, especially during the first few weeks after planting. Once established, they can tolerate some drought but benefit from regular watering, particularly during dry periods. Avoid overwatering, which can lead to root rot.
Cassava leaves, a nutritional powerhouse, are a versatile addition to your garden and meals. They can be used in various dishes, from soups to stews, adding a unique flavor and nutritional value. Just like knowing the right time to sow your grass seeds for a lush lawn, as outlined in this comprehensive guide on How to Achieve a Perfect Lawn by Timing Your Grass Seed Sowing Correctly , understanding the optimal conditions for growing cassava leaves is crucial for maximizing their yield and nutritional content.
Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, incorporating cassava leaves into your culinary repertoire is a rewarding and healthy endeavor.
- Fertilizing:Cassava plants are heavy feeders and benefit from regular fertilization. Apply a balanced fertilizer, such as 10-10-10, every 4-6 weeks during the growing season. You can also use organic fertilizers like compost or manure.
- Weeding:Keep the area around the cassava plants free of weeds, which compete for nutrients and water. Regular weeding helps to promote healthy growth.
- Harvesting:Cassava leaves can be harvested when they are about 15-20 cm (6-8 inches) long. Harvest the leaves by cutting them just above the stem, leaving some leaves on the plant for continued growth.
Preventing Pests and Diseases
Cassava plants are susceptible to various pests and diseases, but proper care can help minimize these issues. Here are some common pests and diseases and how to prevent them:
- Cassava mealybug:This pest feeds on the sap of the cassava plant, causing stunted growth and leaf discoloration. To prevent mealybugs, maintain good hygiene in the garden, remove infected leaves, and consider using natural insecticides like neem oil.
- Cassava mosaic disease:This viral disease causes yellowing and mosaic patterns on the leaves, reducing yield. Prevention includes planting disease-free cuttings, controlling whiteflies (which transmit the virus), and using resistant varieties.
- Cassava root rot:This fungal disease attacks the roots, causing them to rot and leading to plant death. Prevention includes avoiding overwatering, ensuring good drainage, and using disease-free planting material.
Incorporating Cassassa Leaves into Your Meals
Cassava leaves, a nutritional powerhouse, offer a delicious and versatile addition to your diet. They can be incorporated into various dishes, adding a unique flavor and a boost of essential nutrients. From simple stir-fries to flavorful soups, the possibilities are endless.
Methods of Preparing Cassava Leaves
Here’s a table outlining different ways to prepare cassava leaves, showcasing their versatility:| Method | Description | Notes ||—|—|—|| Boiling | Cassava leaves are boiled in water until tender. This method is simple and preserves the leaves’ nutrients. | Boiling can be done with a little salt or other seasonings for added flavor.
|| Steaming | Cassava leaves are steamed until tender. This method helps retain the leaves’ vibrant green color and delicate flavor. | Steaming can be done with aromatics like ginger or garlic for a more flavorful result. || Stir-frying | Cassava leaves are stir-fried with other vegetables, meat, or tofu.
This method creates a flavorful and quick dish. | Stir-frying requires a hot wok and quick cooking to ensure the leaves remain tender and crisp. || Soups | Cassava leaves are added to soups, stews, and broths for a hearty and nutritious meal.
| Cassava leaves can be added towards the end of cooking to retain their texture and flavor. |
Traditional Cassava Leaf Recipes
Cassava leaves are a staple ingredient in many cuisines worldwide, featuring in traditional dishes passed down through generations. Here are a few examples:* Egusi Soup (Nigeria):This hearty soup features cassava leaves, melon seeds, and a variety of vegetables, creating a flavorful and nutritious meal.
Pounded Yam with Edikang Ikong Soup (Nigeria)
A popular dish in Southern Nigeria, this soup features cassava leaves, waterleaf, and seafood, creating a rich and flavorful meal.
Lula (Philippines)
Just as you can propagate a beautiful rose garden from cuttings, How To Propagate Roses From Cuttings: Expert Insights for Beautiful Blooming , you can easily grow your own supply of cassava leaves. These nutrient-rich greens are a versatile addition to your garden, providing a delicious and healthy source of vitamins and minerals.
From stir-fries to soups, cassava leaves add a unique flavor and texture to your meals, making them a valuable addition to any kitchen.
This dish features cassava leaves cooked with coconut milk, shrimp, and spices, creating a unique and aromatic dish.
Sinangag (Philippines)
This popular Filipino dish features garlic fried rice with cassava leaves, creating a flavorful and hearty breakfast.
Banh Xeo (Vietnam)
This crispy crepe features cassava leaves, turmeric, and coconut milk, creating a flavorful and colorful dish.
Preserving and Storing Cassava Leaves
To preserve cassava leaves for later use, consider these methods:* Freezing:Blanch cassava leaves in boiling water for a few minutes, then drain and cool completely. Pack the leaves in freezer-safe bags and store in the freezer for up to 3 months.
Drying
Spread cassava leaves on a drying rack in a well-ventilated area, away from direct sunlight. Once dry, store the leaves in airtight containers in a cool, dark place.
The Health Benefits of Cassava Leaves: Cassava Leaf Magic: How To Incorporate This Nutritious Green Into Your Garden And Meals
Cassava leaves, a staple in many African and Asian cuisines, are more than just a leafy green. They are a nutritional powerhouse packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that offer a wide range of health benefits. Consuming cassava leaves can contribute to a healthier lifestyle and may even help prevent chronic diseases.
The Role of Antioxidants in Cassava Leaves
Antioxidants are essential compounds that protect our bodies from damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage cells and contribute to aging and disease. Cassava leaves are rich in antioxidants, including flavonoids, phenolic acids, and vitamin C.
These antioxidants help neutralize free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and promoting overall health.
- Improved Digestion:Cassava leaves are a good source of dietary fiber, which aids digestion by adding bulk to stool and promoting regular bowel movements. This can help prevent constipation and other digestive issues.
- Enhanced Immunity:The vitamin C content in cassava leaves supports the immune system, helping the body fight off infections and diseases. Vitamin C is also crucial for the production of collagen, a protein that helps maintain healthy skin, bones, and blood vessels.
- Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases:Research suggests that the antioxidants in cassava leaves may help reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and diabetes. For example, studies have shown that flavonoids in cassava leaves may help lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of heart disease.
Incorporating Cassava Leaves into a Balanced Diet
Cassava leaves can be incorporated into a balanced diet in various ways. They can be cooked and eaten as a side dish, added to soups and stews, or used in salads.
- Soups and Stews:Cassava leaves can be added to soups and stews for a nutritious and flavorful boost. They can be cooked with other vegetables, meats, or beans to create hearty and satisfying meals.
- Salads:Cassava leaves can be added to salads for a unique and healthy twist. They can be combined with other leafy greens, vegetables, and fruits for a refreshing and nutrient-rich salad.
- Side Dishes:Cassava leaves can be cooked as a side dish by steaming, boiling, or frying. They can be seasoned with spices, herbs, or sauces for a flavorful and nutritious accompaniment to any meal.
Last Word

Unlocking the magic of cassava leaves is a journey that rewards you with both delicious meals and a boost to your health. Whether you’re captivated by their nutritional prowess or intrigued by their culinary versatility, we hope this exploration has inspired you to embrace this vibrant green.
So, go ahead, plant your own cassava patch, experiment with different recipes, and experience the magic of cassava leaves for yourself.
User Queries
Can I eat cassava leaves raw?
It’s best to cook cassava leaves before eating them. Raw cassava leaves contain toxins that can cause digestive issues. Cooking removes these toxins and makes the leaves safe for consumption.
How long do cassava leaves last in the refrigerator?
Fresh cassava leaves can be stored in the refrigerator for up to 3-4 days. To preserve them for longer, you can blanch them and freeze them for several months.
Are cassava leaves suitable for vegetarians and vegans?
Yes, cassava leaves are a great source of plant-based protein and nutrients, making them suitable for vegetarian and vegan diets.
What are the best ways to preserve cassava leaves?
Cassava leaves can be preserved by blanching and freezing, drying, or pickling. Each method offers a different shelf life and flavor profile.
